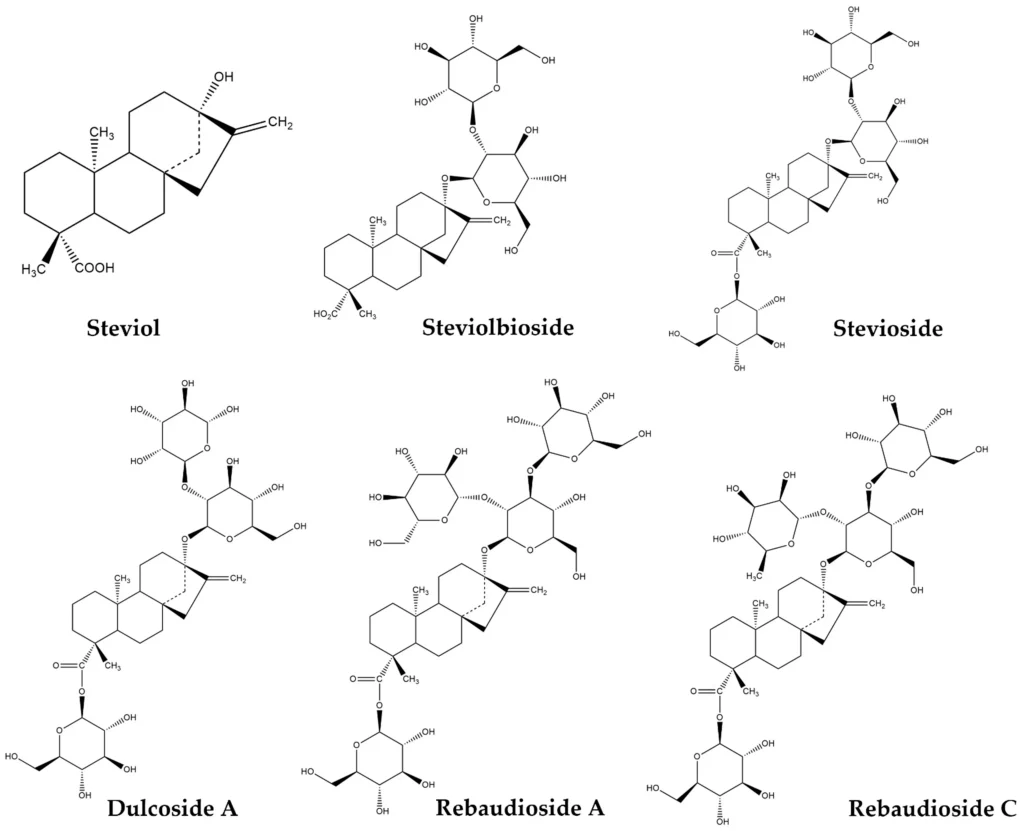
Recent studies suggest that stevia’s anti-cancer properties may offer a new ray of hope in the battle against aggressive cancers like pancreatic cancer. Researchers from Hiroshima University have discovered that fermented stevia extract, derived from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant, exhibits remarkable disease-fighting capabilities. This natural sweetener, often overlooked for its health benefits, is showing promise in laboratory settings where it demonstrated enhanced antioxidant activity and cytotoxic effects against cancer cells. As scientists delve deeper into stevia research, the potential for utilizing this sweetener as a viable option in cancer treatments is becoming increasingly intriguing. With the rise of interest in natural sweeteners and their possible applications in fighting diseases, stevia extract is emerging as a contender worth discussing in the context of health and wellness.
Exploring the therapeutic potential of natural sweeteners like stevia, particularly in relation to their role in cancer prevention, reveals exciting possibilities. Recent investigations into fermented stevia reveal its effective properties against malignancies, especially pancreatic tumors. This innovative approach shifts the focus on how common ingredients can potentially serve as powerful tools in modern medicine. Stevia, traditionally celebrated as a sugar substitute, is now under the microscope for its potential to transform cancer treatment paradigms. By examining the interactions and alterations in plant extracts, we may unlock new pathways to developing effective therapies.
The Potential of Stevia Extract in Cancer Treatment
Recent research has unveiled a promising aspect of stevia extract, particularly its potential in combating aggressive forms of cancer such as pancreatic cancer. The study conducted by Hiroshima University highlighted that when fermented with specific bacterial strains, stevia leaf extract demonstrated significantly enhanced anti-cancer properties. This discovery aligns with the ongoing search for natural sweeteners with health benefits that can aid in disease management, suggesting that stevia could play a larger role in cancer treatment as researchers explore its modified forms.
Stevia extract, a common zero-calorie sweetener, is already popular among health-conscious individuals. However, the implications of its fermented variant could be revolutionary. By transforming the extract through fermentation, researchers found an increase in antioxidant activity, which is crucial in fighting oxidative stress associated with cancer progression. This research invites further exploration into natural alternatives in medicine, with stevia potentially positioning itself as a key player in the quest for effective treatments.
Fermented Stevia and its Health Benefits
Fermented stevia is emerging as a subject of interest within the scientific community due to its unique health benefits, especially its impact on cancer cells. The fermentation process not only enhances the extract’s potency but also increases its bioavailability. As a natural sweetener, it offers the dual benefit of satisfying sweetness cravings while potentially possessing health-enhancing properties that could aid in cancer treatment. This positions fermented stevia as a fascinating alternative in the landscape of dietary supplements and therapeutic agents.
Moreover, the shift towards utilizing fermented stevia in health sciences emphasizes the importance of natural ingredients in treating serious diseases. The findings from Hiroshima University suggest a future where natural sweeteners like stevia could be integral to cancer care protocols. As researchers continue to explore the fermented extract’s capabilities, there’s potential for it to be integrated into clinical practice, offering new hope for pancreatic cancer patients and emphasizing the necessity of ongoing stevia research.
Understanding the Mechanisms of Stevia’s Anti-Cancer Properties
Understanding how stevia extract interacts with cancerous cells is crucial to harnessing its potential as a treatment. The research indicates that the fermented extract exhibits cytotoxic effects specifically on pancreatic cancer cells, suggesting that its mechanism of action involves both direct and indirect pathways to inhibit tumor growth. This insight opens the door for further studies to dissect the active compounds responsible for these effects and how they can be maximized in clinical settings to improve patient outcomes.
Additionally, gaining a deeper insight into stevia’s anti-cancer properties could revolutionize current cancer treatments. The current methodologies employed in fighting pancreatic cancer rely heavily on chemotherapy and radiation, but incorporating fermented stevia could offer a complementary approach that mitigates side effects while enhancing treatment efficacy. This represents a significant step towards multi-faceted cancer therapies, integrating more natural and holistic approaches in modern medicine.
Clinical Trials and Future Research on Stevia
As the body of research surrounding the anti-cancer properties of stevia expands, the critical next step will involve rigorous clinical trials. The findings from laboratory studies provide a strong foundation, but the transition to human subjects is essential to ascertain safety, efficacy, and potential side effects. Medical professionals emphasize the importance of caution when interpreting these preliminary results, highlighting that successful laboratory outcomes do not always translate to clinical success.
In navigating the landscape of pancreatic cancer treatment, clinical trials focusing on fermented stevia extract will be pivotal. These trials not only evaluate the effectiveness of stevia-infused therapies but also contribute to a better understanding of how natural products can be integrated into existing treatment paradigms. As more patients seek innovative treatment options, such clinical research will establish whether stevia eventually becomes a staple in oncological treatment protocols.
The Role of Natural Sweeteners in Cancer Therapy
Natural sweeteners like stevia are increasingly being considered for their role in health and wellness, particularly in cancer therapy. Unlike artificial sweeteners, natural alternatives are perceived as safer and more beneficial, potentially supporting patients’ dietary needs while undergoing cancer treatments. The inherent properties of these sweeteners can complement traditional therapeutic approaches by providing essential nutrients while managing side effects related to conventional treatments.
The landscape of cancer care is evolving, and incorporating natural sweeteners like stevia into treatment regimens reflects a broader trend towards integrative medicine. With rising interest from both patients and healthcare providers in the benefits of natural compounds, exploring their implications in cancer treatment is not only timely but necessary. This highlights the importance of ongoing research in establishing clear guidelines on how these natural substances can be most effectively used in clinical practice.
Stevia Research: What We Need to Know
The recent surge in research on stevia underscores a growing recognition of its potential health benefits. Studies like those from Hiroshima University suggest that while stevia may not offer direct anti-cancer properties in its original form, modifications such as fermentation may unlock its therapeutic potential. As scientists continue to explore and document these changes, creating a clear picture of stevia’s capabilities in cancer treatment becomes increasingly important.
Additionally, the dialogue surrounding stevia research will benefit from cross-disciplinary collaboration. By uniting botanists, oncologists, and nutritionists, insights into the plant’s effects on the human body can inform better therapeutic strategies. Partnering with experimental trials and peer-reviewed studies will enable a holistic understanding of how stevia can be employed in future cancer treatments, offering a hopeful avenue for patients seeking alternatives.
The Safety and Side Effects of Fermented Stevia
As promising as the initial findings about fermented stevia may seem, patient safety remains a top priority. Experts caution that since these studies are still in preliminary phases and have not yet included human subjects, understanding the full spectrum of potential side effects is crucial. While the transformation through fermentation may enhance benefits, it could also introduce unforeseen risks that need thorough investigation before clinical application.
Furthermore, ongoing monitoring and assessment during clinical trials will be essential to evaluate patient responses to fermented stevia extract. Establishing safety profiles will allow healthcare providers to make informed decisions and provide guidance to patients navigating their treatment options. Ultimately, ensuring that the benefits of using fermented stevia outweigh any potential risks will be critical for its acceptance in integrated cancer therapies.
Exploring Patient Perspectives on Stevia as Treatment
With the emergence of new treatments based on stevia, it is essential to consider patient perspectives regarding its use in cancer care. Many patients seek natural alternatives and tend to gravitate towards treatments that align with their desire for holistic health management. Understanding their views on incorporating fermented stevia into their treatment options can provide valuable insights that influence how healthcare providers approach this emerging field.
Moreover, engaging patients in discussions about innovative therapies, including stevia extract, will foster collaboration between them and their healthcare teams. Feedback, preferences, and concerns surrounding the use of natural sweeteners in treatment will help shape future studies and clinical practices. As patient involvement grows, so does the potential for more personalized approaches, ultimately enhancing the quality of care in oncology.
The Future of Sweeteners in Oncology
The exploration of sweeteners such as fermented stevia in oncology presents a promising frontier in cancer treatment. As research continues to unveil the potential anti-cancer properties of natural substances, the integration of these findings into clinical practice may redefine treatment paradigms. The evolution of sweeteners from mere dietary supplements to powerful therapeutic agents highlights the importance of continued investment in research and development in this area.
In conclusion, the future of oncology may very well be influenced by our understanding and utilization of natural sweeteners. With insights from studies on stevia paving the way for broader discussions about natural products in medicine, patients could benefit from groundbreaking therapies that not only treat illness but also enhance overall wellbeing. Embracing this potential could foster a new age of integrative cancer care, bringing hope and healing to patients around the world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the anti-cancer properties of stevia extract based on recent research?
Recent studies have indicated that fermented stevia extract has significant anti-cancer properties, particularly against pancreatic cancer cells. Researchers found that this extract exhibits enhanced antioxidant activity and cytotoxicity, making it a promising candidate for pancreatic cancer treatment.
Can stevia extract health benefits include fighting cancer?
Yes, stevia extract health benefits are becoming exciting in the context of cancer research. Specifically, fermented stevia has shown potential in laboratory studies to combat pancreatic cancer cells, showcasing its unique anti-cancer properties.
How does fermented stevia impact pancreatic cancer treatment?
Fermented stevia extract has shown to enhance activity against pancreatic cancer in lab settings. The fermentation process significantly boosts the extract’s efficacy in preventing the growth of cancer cells, indicating its potential role in future pancreatic cancer treatment strategies.
What does current stevia research say about its role in cancer prevention?
Current stevia research highlights significant findings where fermented extracts of stevia contribute to inhibiting pancreatic cancer cell growth, suggesting that natural sweeteners like stevia may play a role in cancer prevention efforts.
Are there any side effects associated with using stevia as a natural sweetener for cancer?
While initial studies on fermented stevia show promise for anti-cancer applications, there are cautions regarding potential side effects or toxicity due to the chemical alterations involved in fermentation. Further research is necessary to assess safety in human subjects.
What makes fermented stevia a candidate for cancer treatment?
Fermented stevia is considered a candidate for cancer treatment due to its significantly enhanced potency against cancer cells. The fermentation process transforms the natural sweetener, allowing it to demonstrate improved antioxidant and cytotoxic effects specifically against pancreatic cancer.
What should I consider before using stevia for cancer-related health benefits?
If you’re considering stevia for its potential cancer-related health benefits, it’s important to consult with healthcare professionals. As current research focuses on laboratory findings, patient-specific outcomes and effects are still unknown and require further investigation.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Findings | Fermented stevia extract shows potential anti-cancer properties against pancreatic cancer cells. |
| Research Institution | Hiroshima University, Japan. |
| Mechanism of Action | Fermentation enhances antioxidant activity and cytotoxicity against cancer cells. |
| Expert Opinions | Experts are cautiously optimistic but emphasize the need for further testing and clinical trials. |
| Current Limitations | The study has not been conducted on humans, and altered plants may have unknown effects. |
| Future Directions | Further research needed to test the extract’s effectiveness in clinical settings. |
Summary
Stevia anti-cancer properties have recently gained attention as new research suggests that fermented stevia extract may have the potential to combat aggressive pancreatic cancer. Although initial findings from Hiroshima University indicate promising anti-cancer effects, experts emphasize caution due to the study being laboratory-based and not yet tested on humans. As stevia extract alone has not shown efficacy against cancer, further research and clinical trials are essential to determine its true potential in cancer treatment. With ongoing studies, there is hope this natural sweetener could lead to breakthroughs in managing pancreatic cancer.