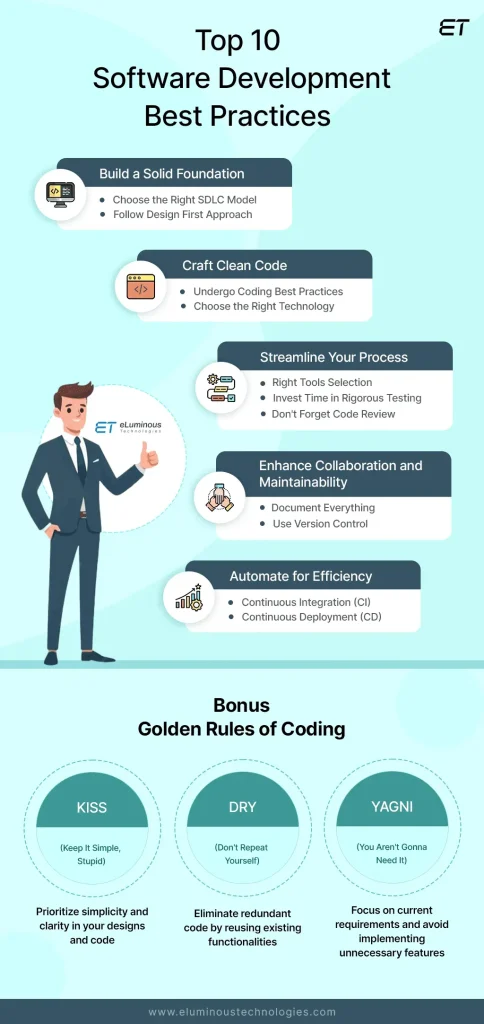
Software development best practices shape how teams deliver reliable, scalable, and secure software in today’s fast-moving ecosystems. By establishing clear guidelines and consistent workflows, organizations reduce friction and improve maintainability across diverse tech stacks. They also guide teams toward high-quality outcomes through automation and iterative feedback. From versioning and automated build-and-deploy pipelines to governance, these approaches help reduce defects and accelerate delivery. Applied thoughtfully, they align team goals, shorten feedback loops, and set a foundation for scalable software projects.
Viewed through an engineering lens, the topic becomes a disciplined craft that blends people, processes, and tooling to deliver value consistently. Teams emphasize coding standards, robust testing strategies, and quality checks across the software lifecycle to prevent defects early. This approach also relies on peer feedback, documented guidelines, and automated verification to keep code healthy and deployments reliable. By aligning development activities with integrated pipelines and observable metrics, organizations can ship faster without sacrificing stability. In short, software engineering best practices translate the same goals into a language that emphasizes quality, collaboration, and continual improvement.
Software Development Best Practices for Modern Teams: Coding Standards, QA, and Code Reviews
The world of software development benefits when teams adopt software development best practices as a disciplined, repeatable approach. Core elements like coding standards help teams write consistent, readable code, while code review processes enable knowledge sharing and early defect detection. Incorporating testing and QA best practices from the start reduces risk and produces more reliable software, aligned with the chosen software development methodologies.
Automation and orchestration, including continuous integration and delivery, turn best practices into fast, repeatable workflows. When teams commit small, well-tested changes and rely on automated validation, feedback loops shrink, reviews stay focused, and maintainability improves across the codebase.
From Methodologies to Delivery: Aligning Software Development Methodologies with CI/CD and Testing Excellence
Selecting and aligning software development methodologies—whether agile, Scrum, Kanban, or hybrids—with practical practices ensures a coherent delivery cadence. This alignment supports predictable planning, backlog refinement, and continuous improvement, while weaving in testing and QA best practices and robust code review processes to catch issues early.
A strong CI/CD foundation accelerates releases without sacrificing quality. By automating builds, tests, and deployments, teams enforce coding standards, enforce security checks, and maintain test coverage. The result is reliable, observable software delivery where feedback is fast and decisions are data-driven.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are software development best practices, and how do coding standards, testing and QA best practices, and CI/CD contribute to quality and speed?
Software development best practices are repeatable, evidence-based techniques that help teams write better code, catch issues earlier, and reliably deliver value. They include coding standards, which improve readability and reduce defects; testing and QA best practices, which enable early and frequent validation across unit, integration, and end-to-end levels; and CI/CD, which automates builds, tests, and deployments for faster, safer releases. Aligning these with your software development methodologies (e.g., Agile, Scrum, Kanban) creates a predictable workflow, promotes collaboration, and lowers risk.
What practical steps should teams take to adopt software development best practices in 2025?
Define and document coding standards with a living style guide and automated tooling; build a robust testing strategy (unit, integration, and end-to-end) with automated tests in the CI/CD pipeline; implement a clear CI/CD workflow with automated builds, tests, deployments, and gates; establish a predictable code review process with checklists and timely feedback; invest in instrumentation and observability to diagnose issues quickly; integrate security checks early and enforce least-privilege access; maintain architecture diagrams and runbooks; measure progress with meaningful metrics (cycle time, deployment frequency, change failure rate) and iterate based on feedback.
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Definition |
|
| Coding Standards |
|
| Methodologies |
|
| Quality Assurance |
|
| Automation & CI/CD |
|
| Code Reviews |
|
| Documentation & Knowledge Sharing |
|
| Security, Reliability, Maintainability |
|
| Practical Steps |
|
| Measuring Success & Pitfalls |
|
| Case Studies |
|
| Best Practice Checklist |
|
Summary
Software development best practices are a framework for building better software with less risk and more predictability. By embracing coding standards, appropriate methodologies, testing and QA practices, continuous integration and delivery, and strong code-review processes, teams can deliver high-quality software faster and more reliably. The journey toward excellence is ongoing: regularly review your practices, incorporate feedback, and adjust to evolving business needs. When teams commit to these principles and make them a daily habit, they create a sustainable path to success in any tech landscape.