An ultra-low latency gaming setup is not about a single flashy component; it’s about a carefully balanced stack where network, hardware, display, and software work in harmony, with each layer finely tuned to minimize signal travel time, suppress jitter, and translate your micro-actions into immediate, cinematic feedback across diverse games and playstyles. When every millisecond counts, players notice the difference in input responsiveness, precision of aiming, and the overall smoothness of motion, whether they’re lining up a headshot in a competitive shooter or carving through a blistering race, because the total end-to-end latency shapes how confident you feel behind every button press, how quickly your character reacts, and how natural the game world feels under pressure. This guide shows how to optimize each layer—network, hardware, display, and software—through a practical, methodical plan that begins with a robust network backbone and progresses outward to processing efficiency, GPU timing, frame pacing, driver and firmware updates, and the display pipeline, all while tracking consistency, reliability, and measurable improvements in real-world play. A core part of the plan emphasizes reliable connections, fast processors, lean background tasks, high-speed storage, and a display path that minimizes frame-time variance, ensuring inputs translate to on-screen actions with minimal lag. Pair that with a high monitor refresh rate, low input lag panels, and careful cable management to maximize visual clarity and minimize the time between render and display, building a foundation for faster, more confident plays across genres.
In the broader sense, this topic can be framed as minimizing end-to-end delay, reducing input lag, and improving frame-time stability, all aimed at creating a more responsive and predictable gaming experience. Think of it as optimizing how data travels from your controller to the game and back to the screen, aligning processing speed with display timing so reactions feel instantaneous. Latency-focused terms you may encounter—LSI-aware and related—include network delay management, ping optimization strategies, and QoS-driven traffic shaping, but they all point to the same core goal: a smoother, more reliable session. Practical steps in this mindset include enabling QoS, wiring your gaming device directly to the router, choosing a monitor with a fast response time and high refresh rate, and trimming background services that siphon CPU cycles. In the end, the payoff is not just faster pixels but a cohesive, dependable feel that helps you stay synchronized with the game world across genres.
ultra-low latency gaming setup: Core Pillars for Instant Response
An ultra-low latency gaming setup is a holistic, system-wide approach where network, hardware, display, and software work in harmony to shave milliseconds from every step of the path from input to action. The central goal is reducing gaming latency across the stack: a reliable wired ethernet path, a capable low latency gaming router, a fast CPU/GPU, fast storage, and a monitor with a tight response. Each link in the chain matters, because a slow link—even if the rest is fast—will be felt as input delay or stutter.
Concrete actions start at the network: run a dedicated Ethernet cable from the router to your PC or console, use shielded cables to minimize EMI, and avoid daisy-chaining devices through power strips. Pair this with a low latency gaming router that supports QoS and regularly updated firmware to prioritize game traffic and reduce wired ethernet latency. On the server and device side, close background tasks and ensure drivers are current to minimize processing delays, then test latency with in-game counters and external ping tests to validate improvements in reducing gaming latency and ping optimization for gaming.
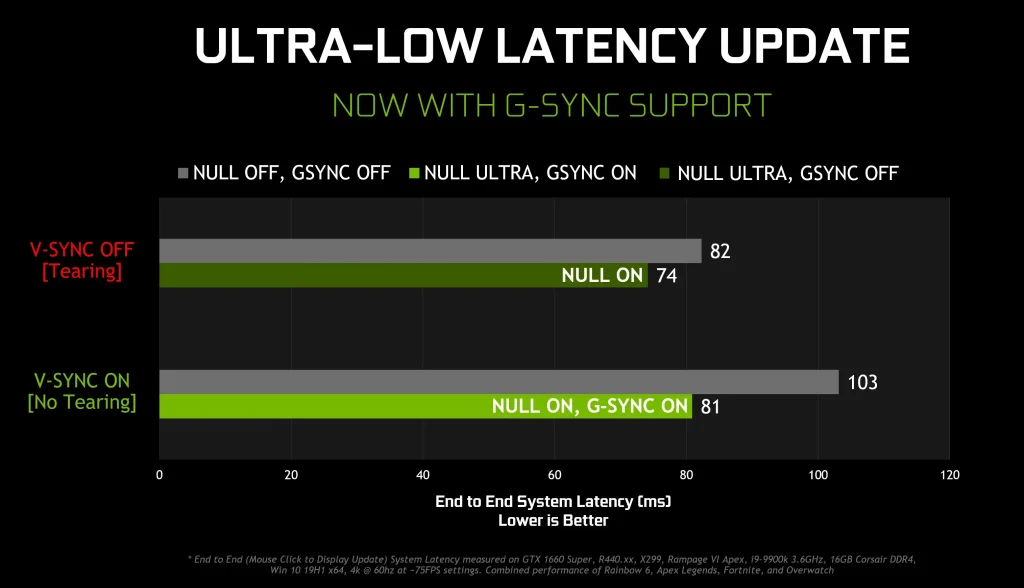
Reducing Gaming Latency: Monitor Refresh Rate, VRR, and Networking Excellence
Display side optimization concentrates on monitor refresh rate and input response. Choose a monitor with a high refresh rate (120 Hz or more) and a low GTG response time, and enable VRR (AMD FreeSync or NVIDIA G-SYNC) to reduce stutter and frame drops that can resemble latency. A display with low input lag works in concert with a fast GPU to ensure each button press translates to visible action with minimal delay.
Networking and software refinements further lower latency. Use QoS to prioritize game traffic, select a high-performance router designed for gaming, and keep firmware current to reduce ping variability. If possible, route the gaming device on a dedicated 1 Gbps LAN port, and maintain wired ethernet latency by avoiding congested Wi‑Fi and extra hops. In addition, optimize settings in-OS and in-game (disable V-Sync if possible, enable VRR, and minimize background processes) to support a smooth, responsive experience while pursuing ping optimization for gaming.
Frequently Asked Questions
In an ultra-low latency gaming setup, how can wired ethernet latency, a low latency gaming router, and monitor refresh rate contribute to reducing gaming latency and improving ping optimization for gaming?
An ultra-low latency gaming setup minimizes delay across network, hardware, display, and software. Start with wired ethernet latency: use shielded cat6a/cat7 cables on a dedicated run to reduce jitter, and avoid daisy-chaining devices. Pair this with a low latency gaming router that supports QoS and timely firmware updates, and assign high priority to your gaming device to improve ping optimization for gaming. Ensure your monitor offers a high refresh rate (120 Hz+) and low native input lag, and enable VRR where supported to reduce display latency. Keep drivers current, close unnecessary background apps, and test with in-game latency counters and ping tests to verify improvements.
What practical steps should I take in an ultra-low latency gaming setup to maximize monitor refresh rate and minimize input/display latency, while ensuring effective ping optimization for gaming?
Begin with a wired Ethernet connection and a router that prioritizes gaming traffic to boost monitor refresh rate benefits and overall latency. Configure the monitor for its native resolution and a high refresh rate, enable VRR, and disable V-Sync unless absolutely needed to minimize input lag from the display pipeline. Optimize software by enabling Game Mode, updating GPU/network drivers, and closing background processes that compete for CPU time. Use ping tests to your game server region and in-game latency counters to measure input-to-display timing, then adjust router QoS priorities and display settings based on real measurements for consistent, snappy performance.
| Pillar | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Network & Connection | – Latency is the sum of network, input, render, and display delays. – Prefer wired Ethernet to reduce variability. – Use shielded Cat6a/7 for long runs if needed. – Avoid daisy-chaining devices; keep a clean, hard-wired topology. – If you must use Wi‑Fi, use 5 GHz / Wi‑Fi 6 with strong signal and minimal interference. |
| Routing & QoS | – Use a low-latency router with QoS to prioritize game data. – Use a 1 Gbps LAN port for your gaming device where possible. – Keep firmware up to date and consider gaming-optimized routers. – Consider a separate guest network to reduce contention on the main network. |
| Display Latency | – Choose a monitor with high refresh rate (120 Hz+) and low response time (1–4 ms GTG). – Enable VRR (FreeSync / G-Sync) if supported. – Favor displays with low input lag and minimal post-processing. – Run at native resolution and matching refresh rate when possible. |
| Hardware Performance | – A capable CPU/GPU, fast storage, and minimized background tasks help reduce frame-time spikes. – Ensure drivers and firmware are up to date. – Maintain a lean software stack to prevent processing delays. |
| Software Tuning | – Update GPU, network, and chipset drivers. – Enable Game Mode or a balanced/performance power profile. – Close unnecessary background apps during gaming. – Disable latency-increasing features (e.g., V-Sync in fast games) unless needed; enable VRR where possible. |
| Measuring & Validation | – Run network latency tests (ping, jitter) and use traceroute to verify stability. – Use in-game latency counters or frame-time tools to measure input-to-display. – Validate with real matches and look for spikes under load. |
| Step-by-step Plan | – Audit your current setup and note latency hotspots. – Upgrade to wired Ethernet where possible; replace aging cables. – Invest in a router with QoS and firmware support; configure priorities. -Choose a fast monitor with VRR and low input lag. -Tweak in-game settings to minimize input lag and keep software lean. -Validate improvements with multiple gaming sessions and adjust. |
| Long-Term Benefit | – A well-tuned ultra-low latency system yields more consistent reactions, better timing, and greater confidence in competitive play across genres. – The payoff comes from steady, immediate feel rather than chasing peak FPS alone. |