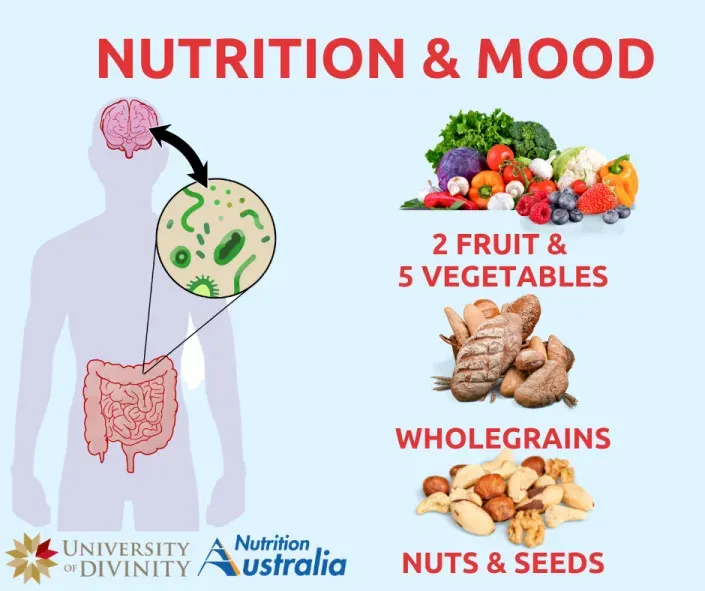
Nutrition for energy and mood is more than a catchphrase; it is a practical framework for selecting everyday foods that support sustained vitality, steady focus, and a resilient emotional state, so you can meet work, study, and life with clarity, motivation, and calm even during back-to-back meetings, long commutes, or late-night deadlines, without sacrificing balance or sleep. When you eat with this goal, you are not simply counting calories; you are influencing neurotransmitter production, gut health, sleep quality, and hormonal balance, thereby shaping energy fluctuations and mood patterns across a typical day, supporting concentration at the keyboard, patience during frustrated moments, and resilience when stress spikes. This approach highlights energy-boosting foods, mood-boosting nutrients, and a diet for sustained energy that smooths blood sugar swings, supports cognitive performance, and keeps fatigue and irritability at bay through balanced meals, regular hydration, thoughtful caffeine timing, and a culture of meals prepared with intention, supporting nutrition and mental health. In practice, you will focus on the right macronutrient mix, rich sources of micronutrients, and lifestyle habits that reinforce the biological pathways linking energy and mood, such as steady protein intake, antioxidant-rich produce, omega-3 fats, gut-friendly fermented foods, regular sleep, and redirection of snack choices toward steadier energy. By adopting mindful meal planning, strategic grocery shopping, and a flexible template that adapts to your day, you can translate nutrition science into reliable routines that support energy, mood, and long-term well-being, creating a sustainable habit loop that grows with experience and feedback, enabling ongoing personalization, accountability, and refinement of your approach as you observe what works best for energy and mood in your unique routine.
An LSI-informed framing introduces the topic through alternative terms such as nutritional strategies for vitality, emotional balance, and cognitive stamina. Instead of saying nutrition for energy and mood repeatedly, we discuss brain-friendly nutrition, metabolic fuel for mental performance, and gut-brain communication as a connected system. This approach also ties dietary patterns to mood regulation, energy maintenance, and mental health by highlighting sources like fiber-rich carbohydrates, lean protein, omega-3 fats, and fermented foods that nurture the microbiome. Using related phrases like energy-boosting foods and mood-supporting nutrients in context helps search engines recognize semantic connections while keeping content accessible to readers.
Nutrition for energy and mood: Building a diet for sustained energy and mood-boosting nutrients
Nutrition for energy and mood offers a practical framework for choosing foods that power daily vitality and steady mood. When you select meals that stabilize blood sugar, provide neurotransmitter building blocks, and support gut health, you’re not just chasing calories—you’re shaping brain chemistry, hormonal balance, and resilience to stress. This approach aligns with nutrition and mental health by treating meals as routines that promote calm focus, steady energy, and emotional balance, rather than quick fixes or gimmicks.
To put this into practice, aim for meals that combine complex carbohydrates, adequate protein, healthy fats, and fiber. Include energy-boosting foods like oats, quinoa, beans, leafy greens, and fatty fish; add mood-boosting nutrients such as omega-3s, magnesium, zinc, and B vitamins from nuts, seeds, and fortified grains. Hydration, regular sleep, and mindful caffeine timing further support a diet for sustained energy and mood. The core message remains: no single “superfood” guarantees results—it’s the overall pattern that nurtures both physical vitality and emotional well-being.
Energy-Boosting Foods and Mood-Boosting Nutrients: A practical daily plan
Energy-boosting foods and mood-boosting nutrients work together to support daily performance. By prioritizing complex carbohydrates for lasting energy, high-quality protein for neurotransmitter production, and healthy fats for brain function, you create a diet that dampens energy crashes and irritability. This approach also emphasizes mood-regulating nutrients—omega-3s, magnesium, zinc, iron, and B vitamins—that support cognitive function, sleep quality, and emotional stability, tying into the broader idea of nutrition for energy and mood.
A practical daily plan centers on simple, repeatable meals. Start with a breakfast that blends protein and complex carbs (for example, oats with yogurt and berries), add a protein-rich lunch (such as quinoa with lean chicken and leafy greens), and include fatty fish or flaxseeds for omega-3s at least a few times per week. Snack on nuts, seeds, and fruit to sustain energy between meals, and keep hydration steady with water or electrolyte-balanced drinks. This routine mirrors the diet for sustained energy and uses common foods that support mood-boosting nutrients, while also minimizing sugar spikes that can derail mood.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is nutrition for energy and mood, and which energy-boosting foods should I include for steady energy and mood support?
Nutrition for energy and mood is a practical pattern of choosing foods that stabilize blood sugar, support brain chemistry, and promote gut health. Focus on energy-boosting foods such as oats and other whole grains, legumes, lean proteins, fatty fish, leafy greens, berries, nuts and seeds, and yogurt. These provide a balance of complex carbohydrates, protein, healthy fats, and mood-boosting nutrients like omega-3s, magnesium, B vitamins, zinc, and vitamin D. Aim for regular meals and snacks, adequate hydration, and mindful caffeine timing to maintain steady energy and a positive mood.
Which nutrients support nutrition and mental health, and how can I design a diet for sustained energy and mood-boosting nutrients?
Key nutrients for energy and mood include complex carbohydrates, high-quality protein, omega-3 fats, fiber, magnesium, iron, zinc, B vitamins, vitamin D, iodine, and selenium. Design a diet for sustained energy by pairing a protein source with a complex carbohydrate, healthy fats, and colorful vegetables at each meal. Include foods such as oats, quinoa, beans, fish, eggs, yogurt, leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and fruit; stay hydrated; and plan regular meals and snacks to prevent energy dips that can affect mood. This approach supports both nutrition and mental health through mood-boosting nutrients.
| Section | Key Points | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction |
|
Aims to turn scientific insights into simple, sustainable eating habits. Focuses on overall patterns rather than chasing a single “superfood.” |
| How nutrition influences energy and mood |
|
Biology-driven relationship between what you eat and how you feel. |
| The core nutrients for energy and mental well-being |
|
Core nutrient groups and their roles in energy and mood. |
| Energy-boosting foods and mood-boosting nutrients to include routinely |
|
Practical roster of foods to routinely include for energy and mood. |
| Meal timing and daily patterns that support energy and mood |
|
Structure meals and timing to stabilize energy and mood. |
| Practical strategies for implementing nutrition for energy and mood |
|
Actionable steps to turn knowledge into daily practice. |
| Practical sample day: a menu focused on energy and mood |
|
Concrete day-long example to guide choices. |
| Common myths and practical truths about energy and mood nutrition |
|
Clarifies common misconceptions with practical truths. |
| The big picture: why this matters for everyday life |
|
Overview of long-term impact and daily relevance. |
Summary
Nutrition for energy and mood is a practical, science-backed approach to everyday eating. By prioritizing complex carbohydrates, high-quality protein, healthy fats, and a rich array of fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods, you supply your body with the nutrients it needs to fuel physical activity, cognitive performance, and emotional stability. Mindful meal timing, hydration, and smart caffeine use further reinforce these benefits. Remember that small, consistent changes often yield the biggest long-term results. Start with a simple meal template, plan a few balanced meals for the week, and observe how your energy and mood respond. Over time, you’ll likely notice improved daily vitality, clearer thinking, and a more resilient mood—all rooted in real nutrition for energy and mood.