Aspergillus infection risks have become a pressing concern as global temperatures continue to rise, creating favorable conditions for this dangerous fungus to thrive. Known scientifically as Aspergillosis, infections caused by this fungal mold can pose serious threats to vulnerable populations, particularly those with compromised immune systems. The implications of climate change on health are far-reaching, as warmer, damp environments facilitate the growth of Aspergillus and increase exposure rates among millions. Consequently, the surge in fungal infections not only jeopardizes human health but also impacts livestock and plant health, raising alarms among healthcare professionals and researchers alike. Since conventional antifungal treatments are often challenging to access and less effective against some strains, awareness of these risks is vital for informed health practices.
The threat posed by Aspergillus infections highlights a critical intersection of environmental changes and human health, particularly in regard to fungal diseases. As we grapple with the implications of a warming planet, the rise of conditions conducive to outbreaks of Aspergillosis presents significant challenges, especially for those whose immune systems are already compromised. Such dynamics underscore the importance of examining how climate-related factors foster conditions for harmful fungi and the need for effective interventions. With rising instances of infections correlating with environmental shifts, addressing these issues through improved treatments and awareness could mitigate risks for the most susceptible populations. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of both the resource needs and prevention strategies concerning these fungal pathogens is essential.
Understanding Aspergillus Infections: Causes and Risks
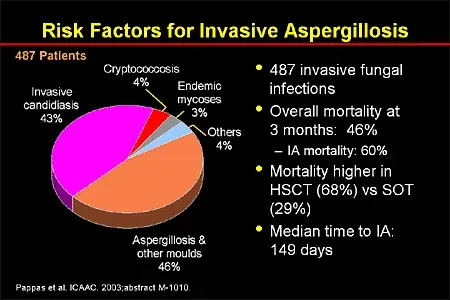
Aspergillus infections pose significant risks primarily due to the prevalence of Aspergillus spores in the environment, which thrive in warm and humid conditions. The risks become particularly concerning as climate change is predicted to increase global temperatures, allowing fungal species like Aspergillus to expand into new habitats. If these environmental changes continue, experts predict a dramatic rise in Aspergillus infections, with a potential increase in prevalence by up to 77% by the year 2100. This alarming trend highlights the urgent need to understand the environmental and health-related factors that contribute to these fungal infections.
The health implications of Aspergillus infections vary significantly among different populations, especially those with compromised immune systems, such as cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. In a healthy individual, inhaling Aspergillus spores may not lead to illness, as a robust immune response typically clears the spores. However, for immunosuppressed patients, the introduction of these spores can result in severe conditions like Aspergillus pneumonia. The immune system’s response to these common environmental fungi is crucial in determining whether an individual will develop a dangerous infection.
The Impact of Climate Change on Aspergillosis Risk
Research highlights a clear link between climate change and the increasing risk of Aspergillus infections. As global temperatures rise, areas that were previously unfavorable for the growth of Aspergillus may become hotspots for fungal proliferation. This shift underscores the potential for wider ecological and health consequences, particularly for susceptible human populations. With climate variability effectively transforming the geographical distribution of fungal species, the healthcare community must prepare for an inevitable rise in cases of Aspergillosis as conditions become more conducive for the fungus to thrive.
Furthermore, the association of climate change with increased fungal infections calls attention to the vulnerability of the immune systems in various populations. With the rise in Aspergillus infections, factors such as age, pre-existing respiratory conditions, and ongoing medical treatments will play crucial roles in determining an individual’s risk level. It remains vital for public health agencies to gather data and assess how changing climates will influence the spread of Aspergillus, enhancing preparedness strategies to mitigate potential outbreaks.
Symptoms and Diagnosing Aspergillus Infections
Diagnosing Aspergillus infections can be particularly challenging due to the wide range of symptoms that may arise. While healthy individuals often show no symptoms after exposure to Aspergillus spores, immunocompromised persons may experience serious respiratory issues. Symptoms include persistent cough, fever, and difficulty breathing, which can easily be mistaken for other respiratory diseases. The complexity in diagnosing Aspergillosis stems from the need for specific medical tests and evaluations that help differentiate it from similar infections.
In cases where Aspergillus is suspected, physicians must rely on advanced imaging tests, lung biopsies, and specific blood tests to confirm the presence of the fungus. Unfortunately, because Aspergillosis often goes unrecognized during initial assessments, it can lead to delayed treatment. Early and accurate diagnosis, paired with comprehensive medical training for healthcare providers, is essential in successfully managing Aspergillus infections and improving patient outcomes.
Preventive Measures Against Aspergillus Infections
Given the environmental persistence of Aspergillus, preventing infection can be particularly challenging. Individuals at highest risk, especially those who are immunocompromised, should take precautionary steps to limit exposure. This includes avoiding activities such as gardening or working with soil until consulting a healthcare professional. Moreover, maintaining indoor humidity levels and ensuring proper ventilation can further reduce the chances of Aspergillus spores proliferating in living environments.
Public health recommendations stress the importance of awareness regarding Aspergillus and its potential health impacts. For those with known vulnerabilities, proactive communication with healthcare providers about risks and preventative strategies is crucial. Enhanced awareness and education regarding Aspergillus infections can empower at-risk populations to adopt preventive measures, ultimately reducing the incidence of severe infections.
Antifungal Treatments for Aspergillosis
Managing Aspergillosis often requires antifungal treatments, which are essential in combating the infection once diagnosed. However, the current antifungal repertoire presents challenges, as some Aspergillus strains have shown increasing resistance to conventional treatments. This escalating resistance calls for a critical evaluation of current antifungal strategies and emphasizes the necessity for ongoing research to develop more effective therapeutic options for Aspergillus infections.
Moreover, healthcare providers need to be vigilant in recognizing potential Aspergillus infections early, as timely administration of antifungal medications can drastically improve outcomes for patients. Incorporating advanced diagnostic technologies and improving training for medical professionals will aid in the early detection of Aspergillosis, ensuring that appropriate antifungal treatments can be delivered without delay.
The Role of the Immune System in Aspergillus Infections
The immune system’s fundamental role in defending the body against Aspergillus infections cannot be overstated. A healthy immune response is typically effective in clearing inhaled spores, preventing the development of Aspergillosis. However, in immunocompromised individuals, such as those undergoing treatments for cancer or autoimmune disorders, the immune system falters, making them significantly more susceptible to invasive fungal infections. Understanding how the immune system interacts with Aspergillus is key to developing targeted treatment and prevention strategies.
Emerging research highlights how an impaired immune response can serve as a gateway for Aspergillus spores to invade bodily tissues, leading to severe conditions like pneumonia. This underscores the importance of monitoring immune function in at-risk populations and developing tailored interventions to bolster the immune response. Addressing the relationship between the immune system and fungal infections may hold the key to reducing the burden of Aspergillus-related illnesses in vulnerable communities.
Climate-Related Trends in Fungal Infections
The growing body of evidence linking climate change to rising fungal infections, particularly Aspergillus, reveals significant trends that warrant attention. As temperatures and humidity levels rise, the prevalence of Aspergillus in various regions is expected to increase, posing a threat to both public health and agricultural practices. Proactive measures, including monitoring these trends and analyzing their impact on health outcomes, will be crucial in managing future risks associated with Aspergillus infections.
Furthermore, with the potential for more pronounced outbreaks in the coming decades, healthcare systems must prepare to address the challenges posed by an increase in climate-related fungal infections. This includes enhancing disease surveillance, advancing medical research into antifungal treatments, and increasing public awareness of the health risks associated with rising temperatures and humidity. The intersection of climate change and fungal infections represents a complex challenge that necessitates interdisciplinary collaboration in terms of research, public health policy, and community education.
Addressing Aspergillus Infection in the Healthcare Sector
In addressing Aspergillus infections within the healthcare sector, a multifaceted approach is necessary to effectively manage and mitigate risks. This includes educating healthcare workers about the risks posed by Aspergillus and implementing robust infection control practices in healthcare establishments. Ensuring that medical professionals are equipped with the necessary training to recognize and diagnose Aspergillus infections can facilitate early intervention and treatment for patients.
Additionally, fostering collaboration among healthcare providers, researchers, and public health authorities will promote better understanding and management of Aspergillus infections. Implementing guidelines for monitoring and responding to Aspergillus risks in clinical settings can significantly enhance patient safety, particularly for vulnerable populations. Continued research into improved diagnostic methods and treatment options will be vital in combating the emerging threat of Aspergillus infections.
Future Implications of Aspergillus Infections
Looking ahead, the implications of rising Aspergillus infections are profound, affecting public health, agriculture, and ecological balance. As climate change progresses, the adaptability of Aspergillus to new environments poses threats not only to human health but also to crops and livestock—further exacerbating the potential for food insecurity. The interconnectedness of climate, health, and agriculture necessitates a comprehensive approach to managing these risks where public policy and practical interventions overlap.
Stakeholders across various sectors must prioritize research focused on the relationship between climate change and fungal infections like Aspergillosis. Collaborative efforts in developing effective prevention strategies, facilitating public health education, and improving healthcare infrastructure will be essential for addressing the dual challenges of climate change and increasing fungal infections. As the world adapts to a changing climate, proactive measures must be taken to safeguard the health of populations prone to Aspergillus infections.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the risks associated with Aspergillus infections like Aspergillosis?
Aspergillus infections, particularly Aspergillosis, pose significant risks for individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing cancer treatment or with chronic lung conditions. Healthy individuals may inhale Aspergillus spores without issue, but for immunocompromised patients, these spores can lead to severe infections like pneumonia and systemic disease.
How does climate change affect Aspergillus infection risks?
Climate change is predicted to exacerbate Aspergillus infection risks as rising temperatures may create ideal conditions for the fungus to thrive. Studies suggest that by 2100, the prevalence of Aspergillus could increase by 77%, potentially exposing millions in temperate regions to higher infection rates from Aspergillosis.
Who is most at risk for serious Aspergillus infections?
Individuals at increased risk for serious Aspergillus infections include those with compromised immune systems, such as patients undergoing chemotherapy, the elderly, and those with pre-existing respiratory conditions like asthma. These groups are more vulnerable to invasive disease caused by Aspergillus.
What preventive measures can reduce Aspergillus infection risks?
To reduce Aspergillus infection risks, especially for immunocompromised individuals, it’s advisable to avoid working with soil, and consult healthcare providers for protective measures. Awareness of Aspergillus exposure and improved training on recognizing symptoms of Aspergillosis among healthcare professionals can also enhance prevention.
What antifungal treatments are available for Aspergillus infections?
There are antifungal treatments available for Aspergillosis, but the diagnosis can often be overlooked. It’s crucial for healthcare providers to recognize symptoms early and consider suitable antifungal medications, particularly as some Aspergillus strains may develop resistance to treatments over time.
Why are Aspergillus infections difficult to treat?
Aspergillus infections are challenging to treat due to difficulties in diagnosis, limited effective antifungal drugs, and the increasing resistance of some Aspergillus strains to these medications. This complexity necessitates ongoing research to develop better diagnostic tools and treatment options.
How can changes in habitat due to climate change impact Aspergillus exposure?
Changes in habitat caused by climate change can significantly increase Aspergillus exposure by expanding the geographical range where the fungus thrives. This shift may lead to more frequent encounters with Aspergillus spores, increasing the risk of infection, especially among susceptible populations.
| Key Point Summary | Details |
|---|---|
| Aspergillus Threat | The emergence of Aspergillus as a potential health risk due to rising global temperatures. |
| Predicted Increase | Estimates suggest a 77% rise in Aspergillus prevalence by 2100, especially in Europe. |
| Impact on Health | Aspergillus can cause infections in immunosuppressed individuals, leading to severe conditions like pneumonia. |
| Vulnerable Populations | Elderly, immunocompromised, and those with asthma are at increased risk. |
| Prevention Challenges | Avoiding Aspergillus is difficult due to its environmental presence, particularly in soil. |
| Need for Research | More research is needed on Aspergillus infections, treatments, and diagnostics. |
Summary
Aspergillus infection risks represent a significant challenge as rising global temperatures may enhance the spread and prevalence of this dangerous fungus. Researchers predict that increasing climate change scenarios could allow the Aspergillus fungus to thrive, elevating the risk of infections, especially in vulnerable populations. Early diagnosis, effective treatments, and a better understanding of the environmental factors contributing to Aspergillus infections are crucial in mitigating these risks.