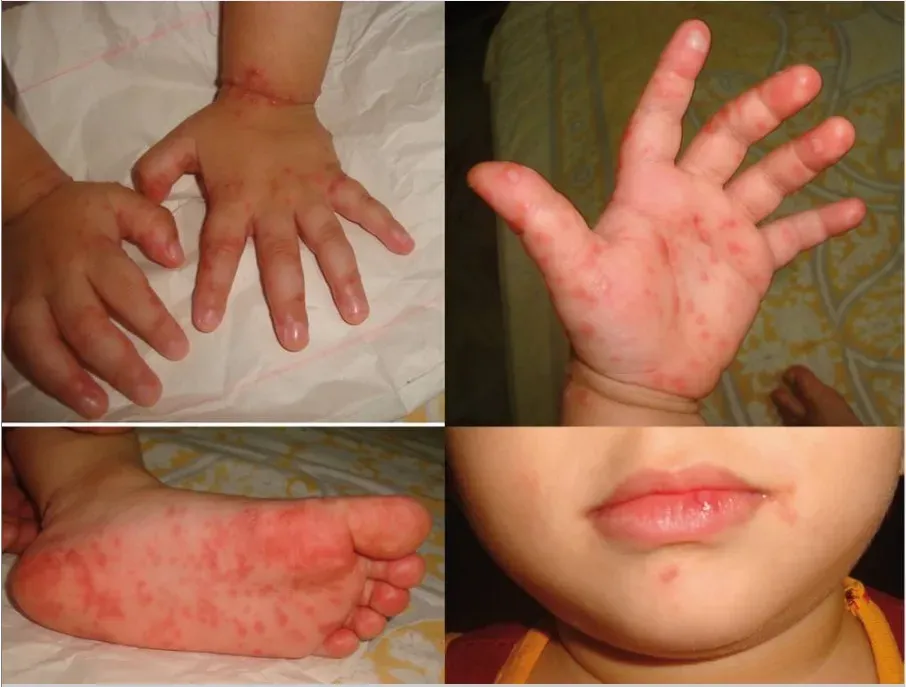
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is witnessing a significant uptick in cases across various regions of the United States, raising concerns among health officials. This highly contagious viral infection primarily affects children under five, though it can impact people of all ages. With HFMD outbreaks being reported in places like Virginia and the U.S. Virgin Islands, understanding HFMD symptoms becomes crucial for early detection and treatment. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) emphasizes hand foot mouth prevention strategies, especially as the illness spreads rapidly in daycare environments. Effective HFMD treatment options predominantly involve managing symptoms, ensuring hydration, and adhering to CDC guidelines to minimize transmission.
The surge in cases of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease, often referred to as HFMD, exemplifies a growing public health concern characterized by notable outbreaks, particularly among young children. This viral ailment is marked by discomforting symptoms that usually include painful sores and rashes, leading to increased demand for effective treatment and prevention strategies. Understanding the risk factors associated with the outbreak of this illness is essential, as well as recognizing the importance of maintaining hygiene practices. The community must remain vigilant about the CDC recommendations for hand foot mouth disease, ensuring children are monitored for any risks of complications that can arise. As awareness spreads, so too does the opportunity for better management and prevention of HFMD.
Understanding Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a viral infection that primarily affects young children, particularly those under the age of five. Characterized by fever, sore throat, and painful mouth sores, the disease presents itself with distinctive rashes or blisters on the hands and feet. According to the CDC, HFMD is highly contagious, spreading through respiratory droplets and contact with infected surfaces. Parents and caregivers should remain vigilant for symptoms, especially during outbreaks, as awareness can help prevent the spread among vulnerable populations.
Despite being deemed mild in most cases, HFMD can lead to serious complications, such as viral meningitis, particularly if caused by certain viral strains like the enterovirus type A6. Symptoms may vary significantly, and adults are increasingly reporting atypical cases with more severe manifestations, highlighting the need for continued education on the disease. Health authorities, including the Pan American Health Organization, stress the importance of vigilance and proactive measures to curtail HFMD outbreaks in communities.
Identifying HFMD Symptoms for Early Treatment
Recognizing the symptoms of HFMD early can significantly impact treatment effectiveness and reduce the spread of the virus. Common signs include fever, mouth sores, and a rash appearing on the palms and soles. In some cases, patients may develop blisters which can be quite painful. If you notice your child exhibiting these symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical advice to confirm the diagnosis and discuss potential treatment options. Monitoring hydration is particularly important since painful sores can hinder fluid intake, leading to dehydration.
Additionally, symptoms can take 3 to 7 days to appear after exposure, which means that children may be contagious even before they show visible signs of illness. Parents should be aware that HFMD can also manifest similarly to other viral illnesses, making it essential to differentiate between conditions. Maintaining an open line of communication with healthcare providers during outbreaks can provide parents with reassurance and guidance on managing their child’s symptoms effectively.
Prevention Strategies Against HFMD Outbreaks
Preventing Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease requires proactive measures, especially in communal settings like daycares and schools. Health professionals recommend frequent handwashing with soap and water, particularly after diaper changes and before meals. Disinfecting common surfaces like doorknobs, toys, and shared utensils is also vital in limiting the spread of the virus. The CDC emphasizes that these preventative measures are the most effective tools parents and guardians have at their disposal to protect their children from HFMD.
It’s equally important to educate children about hygiene practices and the significance of not sharing personal items during outbreaks. Creating a culture of cleanliness in schools and daycare facilities can greatly reduce the incidence of HFMD. As the disease spreads easily among young children, who may have less understanding of these practices, involving staff in regular hygiene protocols and communication is essential for outbreak control.
Exploring HFMD Treatment Options
While Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease typically resolves on its own, there are treatment options available to manage symptoms. Over-the-counter medications can help alleviate pain and reduce fever, making your child more comfortable during recovery. The CDC provides guidelines that suggest staying hydrated is paramount; therefore, offering ice pops or diluted juices can be effective when oral intake is challenging due to mouth sores.
In cases where symptoms worsen or when there is difficulty maintaining hydration, seeking medical attention becomes imperative. Parents should monitor their child for warning signs such as reduced urination or increased lethargy, indicating possible dehydration. Understanding these treatment options is crucial for caregivers to ensure their child navigates through HFMD with minimal discomfort and complications.
CDC Guidelines for Managing HFMD
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides critical guidelines for managing Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease, focusing on both treatment and prevention strategies. These guidelines underline the importance of fostering a clean environment, particularly in daycare settings where outbreaks are more common. Regular cleaning and disinfection of surfaces can significantly reduce the risk of transmission, as the virus can survive on surfaces for extended periods.
Moreover, the CDC encourages parents to stay informed about the symptoms typical of HFMD and to act promptly should any signs arise. If your child is diagnosed with HFMD, keep them home from school or daycare until they are fever-free and feeling better, which helps limit community transmission. Following CDC guidelines not only protects your child but contributes to the well-being of the larger community by controlling the spread of HFMD.
The Growing Concern of HFMD Outbreaks Worldwide
As awareness of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease grows, so does concern regarding the increasing outbreaks reported globally. Recent trends indicate a rise in HFMD cases not only in the United States but also in countries across the world. Public health organizations, including the Pan American Health Organization, recommend that governments enhance their strategies for preventing and controlling HFMD, particularly among young children who are more susceptible.
The emergence of new viral strains has also signified a shift in the patterns of HFMD infections, with adults experiencing symptoms that were previously uncommon. It is essential for communities worldwide to remain vigilant about hygiene practices to aid in slowing the spread of this contagious illness. Sharing knowledge and resources can empower families and schools to effectively combat the surges in HFMD.
Understanding the Impact of HFMD on Children
HFMD primarily affects children, and understanding its impact on this demographic is crucial for parents and caregivers. Young children are particularly vulnerable due to their developing immune systems and closer interactions in daycare or school settings. The symptoms of HFMD can lead to significant discomfort, including painful mouth sores and rashes, which can deter children from engaging in their usual activities. This not only affects their physical health but can also disrupt their emotional well-being.
The psychological effects of illness, including isolation during outbreaks and the anxiety associated with symptoms, should not be overlooked. Parents and educators must support children through this experience by fostering a nurturing environment while they recover. Addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of HFMD can aid children in overcoming these temporary setbacks.
Long-term Implications of HFMD in Adults
While Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease is primarily associated with children, there is a growing awareness of its effects in adults. Recent trends show that adults are increasingly experiencing HFMD, particularly those with close contact with infected children. Symptoms in adults can range from mild to severe, including extensive rashes and other atypical manifestations. Understanding that HFMD is not just a childhood illness is important for broader public health awareness.
Moreover, adults can face long-term implications after contracting the virus, particularly in terms of immunity and susceptibility to recurrent infections. As the incidence of HFMD in adults increases, it is crucial for health practitioners to educate all age groups on prevention and early identification of symptoms. This collective knowledge can empower families to take protective measures and foster healthier environments.
Community Efforts in Combating HFMD Outbreaks
Combating Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease requires a concerted effort from communities and health agencies alike. Local health departments play a pivotal role in monitoring HFMD outbreaks and disseminating information to the public. Community awareness campaigns and educational programs are essential to equip parents with knowledge about HFMD symptoms, prevention, and treatment. Engaging community members in understanding how to protect children can significantly reduce infection rates.
Moreover, collaboration between schools, parents, and health authorities can establish a robust framework for early detection and prompt reporting of potential HFMD cases. Such community efforts pave the way for timely interventions that can help manage outbreaks and return to normalcy sooner. Empowering communities with the right resources and guidance can lead to a healthier future for children affected by HFMD.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)?
Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) primarily presents with symptoms such as blistering sores in the mouth, rashes on the hands and feet, fever, and a sore throat. These symptoms usually appear after an incubation period of three to six days and are most prevalent among children.
How can I prevent Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) in my household?
Preventing Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) involves practicing good hygiene such as frequent handwashing with soap and water, especially after diaper changes or before meals. Cleaning and disinfecting commonly touched surfaces, like doorknobs and toys, is also crucial in breaking the chain of infection.
What treatment options are available for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)?
Treatment options for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) primarily focus on symptom relief. Over-the-counter medications can help manage pain and fever, while ensuring adequate hydration is key. Most cases resolve within a week, but you should consult a doctor if symptoms worsen.
What guidelines does the CDC provide for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)?
The CDC guidelines for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) emphasize the importance of hygiene practices, monitoring symptoms, and staying hydrated. Parents should keep children at home until they are fever-free and feeling well enough to participate in activities without excessive drooling or open sores.
Are there any rising trends in Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) outbreaks?
Recent reports indicate a rise in Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) outbreaks, particularly in children under five. Health officials are monitoring increased cases, with specific attention to outbreaks in areas like Virginia and the U.S. Virgin Islands, where HFMD cases and unusual symptoms are being documented.
What are the potential complications associated with Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)?
The most common complication of Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is dehydration, which can occur due to painful mouth sores interfering with fluid intake. It’s important to seek medical attention if symptoms worsen or if maintaining adequate hydration becomes difficult.
Can adults contract Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD), and how does it manifest in them?
Yes, adults can contract Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD), although it is more common in young children. In adults, HFMD may manifest with unusual symptoms such as extensive rashes and in some cases, nail loss, especially with the rise of certain viral strains.
Is there a vaccine available for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)?
Currently, there is no vaccine available for Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) in the United States. The best prevention remains good hygiene practices and limiting contact with infected individuals or contaminated surfaces.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Increase in Cases | Rising cases of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) reported mainly among children under five, particularly in Virginia and the U.S. Virgin Islands. |
| Symptoms | Symptoms include blistering sores in the mouth, rashes on hands and feet, fever, and sore throat. |
| Transmission | Transmitted through respiratory droplets, contact with blister fluids, contaminated surfaces, and during diaper changes. |
| Treatment | Most cases are mild and resolve within 7-10 days; pain and fever can be treated with over-the-counter medication. |
| Preventative Measures | Frequent hand washing, disinfecting shared items, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals. |
Summary
Hand Foot and Mouth Disease is becoming increasingly prevalent, especially among young children and can lead to serious complications in some cases. It’s essential to understand its symptoms, transmission methods, and treatment options to manage the illness effectively. As HFMD cases continue to rise, maintaining proper hygiene and awareness is crucial for prevention and control, particularly in daycare and school settings.