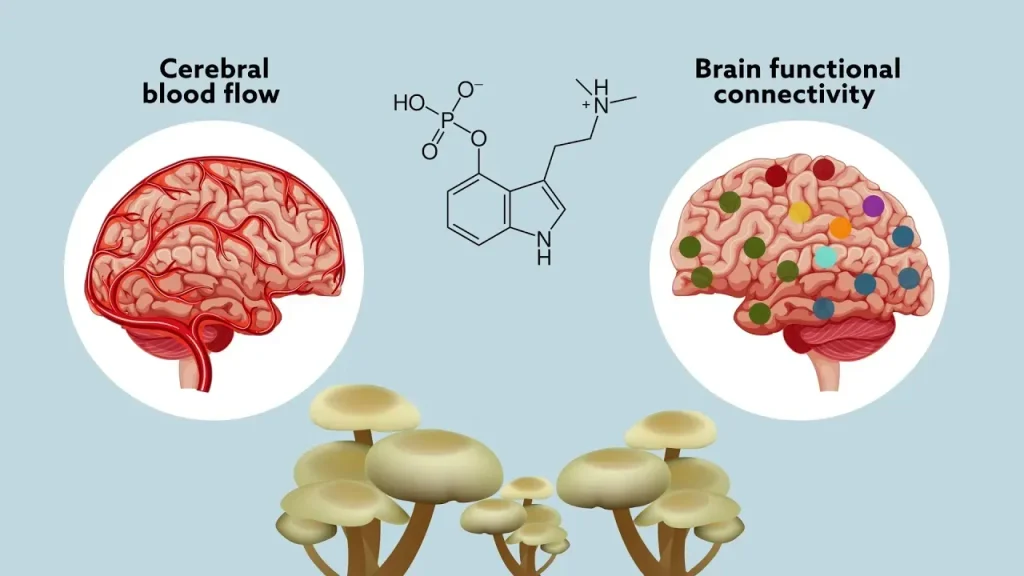
Psilocybin in Parkinson’s Disease is emerging as a potential beacon of hope in the ever-evolving landscape of Parkinson’s treatment. Recent studies reveal that psilocybin, the psychedelic compound famously known as magic mushrooms, may offer significant benefits for patients grappling with this neurodegenerative disease. Research from the University of California San Francisco (UCSF) indicates that psilocybin can enhance mood, cognition, and even motor function in individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s. Given the complex relationship between Parkinson’s and mental health, incorporating psychedelics into therapeutic practices could revolutionize the way we approach the challenges faced by patients. As psychedelic research gains traction, the implications for improving overall quality of life in those with Parkinson’s could be profound.
The exploration of psychedelic compounds like psilocybin for neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s disease marks a significant shift in treatment paradigms. These natural substances, often referred to as magic mushrooms, possess properties that could foster improvements not only in mood disorders but also in the movement difficulties associated with such neurodegenerative ailments. The potential of psilocybin benefits extends beyond alleviating depression and anxiety, suggesting a possible connection to enhancing physical symptoms of Parkinson’s. Understanding the impact of psychedelics within this context paves the way for future studies aimed at developing effective interventions for individuals suffering from debilitating symptoms. Thus, the integration of psilocybin into clinical practice could unlock new avenues for effective Parkinson’s treatment.
Understanding Psilocybin’s Role in Parkinson’s Treatment
Psilocybin, the psychoactive compound found in magic mushrooms, is emerging as a revolutionary approach in the realm of Parkinson’s treatment. As researchers delve deeper into the therapeutic potential of psychedelics, studies conducted at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) highlight psilocybin’s ability to enhance mood and cognition while also improving motor functions in Parkinson’s patients. This novel therapy is particularly significant given that traditional treatments often fall short in alleviating the debilitating mood disorders associated with Parkinson’s disease.
The findings from UCSF’s research indicate that psilocybin may influence the brain’s serotonin receptors, potentially leading to improved dopamine modulation—a critical factor in managing Parkinson’s symptoms. By promoting a sense of well-being, researchers believe psilocybin could not only mitigate depression and anxiety but also contribute to reducing the physical decline often seen in Parkinson’s patients. As understanding grows about the neurochemistry of this psychedelic compound, it offers hope for redefining treatment paradigms for neurodegenerative diseases.
The Impact of Psilocybin on Motor Symptoms and Quality of Life
The recently published study signals a groundbreaking shift in how we approach neurodegenerative disease therapies. Among the notable findings was the unexpected improvement in motor symptoms among participants who received psilocybin treatment. For many patients, overcoming motor dysfunction is crucial, as it significantly impacts their quality of life. This discovery opens up new avenues for research and suggests that psychedelics may have far-reaching effects beyond mood enhancement.
Additionally, the study’s follow-up data revealed that improvements in mood and motor functions persisted even three months post-treatment. This persistent effect is particularly encouraging for those suffering from Parkinson’s as it demonstrates the potential long-term benefits of psilocybin therapy. As we continue to explore its applications, understanding how psychedelics can enhance not only mood but also physical abilities will be vital for future Parkinson’s treatment plans.
Psychedelic Research and Its Future in Parkinson’s Disease
Psychedelic research is gaining traction, and the potential implications for Parkinson’s disease could transform current treatment methodologies. The small-scale pilot study conducted at UCSF sets the stage for larger trials that aim to explore how psilocybin can improve both the cognitive and motor deficits associated with this complex neurodegenerative disease. The researchers are optimistic that by unraveling the mechanisms behind psilocybin’s effects, new therapeutic avenues can be developed for other conditions linked to mental health and neurodegeneration.
As a starting point, it’s imperative that future studies employ rigorous controls and involve larger participant pools to provide conclusive evidence regarding psilocybin’s effectiveness. Meanwhile, there’s an increasing need for regulatory frameworks governing the use of psychedelics in clinical settings to ensure the safety and well-being of patients. There is great optimism about the future of psychedelic therapies, and psilocybin may play a crucial role in reshaping Parkinson’s treatment strategies.
Psychological Benefits of Psilocybin in Parkinson’s Patients
Patients with Parkinson’s disease often face overwhelming emotional challenges due to the neurological impacts of their condition. Psilocybin has shown promise in addressing these psychological aspects, with evidence suggesting improvements in anxiety and depression among users. This is critical since untreated mood disorders not only worsen the quality of life but also exacerbate motor symptoms, reinforcing a cycle of decline.
The positive psychological effects of psilocybin could lead to better overall wellness for Parkinson’s patients, making it a vital area of exploration. Enhanced mental health contributes to improved engagement in therapeutic programs, physical rehabilitation, and social interactions, which are all essential for managing life with neurodegenerative diseases. Continued exploration into the psychological benefits of psilocybin could therefore provide essential insights into comprehensive Parkinson’s treatment approaches.
Evaluating the Safety of Psilocybin in Medical Use
Safety is a paramount concern when introducing any new treatment modality, especially one involving psychedelics like psilocybin. The UCSF study reported that psilocybin was generally well-tolerated, with side effects such as increased anxiety or nausea manageable and not serious. However, the potential for adverse reactions, particularly in individuals with preexisting mental health conditions, necessitates cautious advocacy and a comprehensive understanding of individual patient profiles.
This highlights the importance of having healthcare professionals involved in managing and monitoring the treatment process for patients considering psilocybin therapy. As researchers gather more data on safety and efficacy, it will be crucial to develop specific guidelines that optimize treatment outcomes while prioritizing patient safety. Thus, a careful balance between exploring innovative treatments and ensuring patient well-being remains central to the conversation around psychedelics in medicine.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Psilocybin Research
The encouraging results from initial studies on psilocybin for Parkinson’s pave the way for a new frontier in medical research. As public and scientific interest in psychedelics increases, there is an impetus to investigate their therapeutic properties more rigorously. Ongoing studies must aim for larger sample sizes and varied demographics to truly assess the treatment’s versatility across different populations affected by Parkinson’s and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Moreover, as researchers glean insights from these trials, they may unlock mechanisms that inform the development of next-generation psychedelics. These compounds could offer even more targeted treatments for mood disorders and motor symptoms associated with Parkinson’s. Advocating for funding and support for psychedelic research will be essential to ensure that promising discoveries are not halted prematurely but rather explored for their full therapeutic potential.
Understanding the Connection Between Mood and Motor Function in Parkinson’s
Research illustrates a significant link between mood and motor function in Parkinson’s patients. Mood disorders such as depression and anxiety can accelerate physical decline, making effective psychological treatment crucial for improving overall health outcomes. Psilocybin’s ability to alleviate these mood symptoms could herald a new strategy for managing Parkinson’s, addressing not only the physical but also the emotional and psychological facets of the disease.
By focusing on the intertwined nature of mood and motor function, healthcare providers can develop more integrated treatment plans that enhance the patient’s quality of life. This holistic approach encourages not just medical intervention but also psychological support, creating a comprehensive care model that addresses all dimensions of health for individuals with Parkinson’s.
The Importance of Controlled Research in Psychedelic Treatments
As the field of psychedelic research progresses, the establishment of controlled studies becomes increasingly important. This would allow researchers to draw more definitive conclusions regarding the effectiveness and safety of psilocybin in treating conditions like Parkinson’s disease. It is vital to implement rigorous protocols and control groups to understand how psilocybin compares to traditional treatments and other emerging therapies.
Such studies will not only validate the initial findings regarding psilocybin’s efficacy but will also help in identifying the patient populations that stand to benefit the most. In doing so, researchers can refine dosing regimens, minimize risks, and ultimately contribute to developing a new class of therapeutic agents that could significantly improve life quality for those suffering from neurodegenerative diseases.
Navigating Legal and Ethical Considerations in Psychedelic Research
Psychedelic research, including studies on psilocybin, faces a complex landscape of legal and ethical considerations. As the legal status of psychedelics continues to evolve, it is crucial that researchers remain compliant and conscientious about how studies are conducted and the implications of their findings. Regulatory frameworks need to adapt to allow for the safe exploration of psilocybin’s therapeutic potential while ensuring participant welfare.
Ethical considerations extend beyond legality; they encompass patient consent, disclosure of potential risks, and the responsibility of researchers to communicate findings transparently. By prioritizing ethical standards in research, scientists can foster trust between study participants and the medical community, which is essential for advancing the field. Careful navigation of these issues will ensure that the promises of psychedelic therapy are realized without compromising patient safety and integrity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role does psilocybin play in Parkinson’s disease treatment?
Psilocybin, found in magic mushrooms, has emerged as a promising treatment for Parkinson’s disease. Recent research from UCSF shows that psilocybin can improve mood, cognition, and even motor functions in patients suffering from this neurodegenerative disease.
How does psilocybin affect mood disorders in Parkinson’s patients?
Psilocybin has been shown to alleviate mood disorders such as depression and anxiety in Parkinson’s patients. In a clinical study, participants reported significant improvements in mood symptoms, which are linked to a faster physical decline, indicating psilocybin’s potential in treating these mood dysfunctions.
What are the potential benefits of psilocybin for Parkinson’s disease patients?
Psilocybin may offer various benefits for Parkinson’s disease patients, including enhancements in mood stability, cognitive function, and motor skills. The substance’s ability to modulate serotonin receptors could contribute to these positive outcomes, making it a focus of ongoing psychedelic research.
Are there any side effects associated with using psilocybin in Parkinson’s treatment?
Common side effects of psilocybin in Parkinson’s studies include anxiety, nausea, headaches, and increases in blood pressure. However, these effects were generally mild and did not require medical intervention, highlighting psilocybin’s tolerance among patients.
What do studies say about the safety of psilocybin in neurodegenerative diseases?
Current studies suggest that while psilocybin is generally well-tolerated in patients with Parkinson’s disease, it should be approached with caution. Research is still in the early stages, and it’s essential for patients to consult healthcare professionals before considering psilocybin treatment.
How does psilocybin compare to traditional Parkinson’s treatments?
Unlike traditional Parkinson’s treatments, which may not effectively address mood disorders, psilocybin offers a novel alternative that targets both mood and motor symptoms. Initial studies suggest that psilocybin could supplement existing therapies, providing a comprehensive approach to managing Parkinson’s disease.
What is the future of psilocybin research in Parkinson’s disease?
The future of psilocybin research in Parkinson’s disease looks promising, with larger clinical trials underway to rigorously assess its effectiveness. Researchers aim to gather comprehensive biological data to enhance understanding and optimize psilocybin treatments tailored for individuals with neurodegenerative diseases.
Is it safe for Parkinson’s patients to self-medicate with psilocybin?
Self-medication with psilocybin is not recommended for Parkinson’s patients. Clinical studies are still ongoing, and healthcare providers emphasize the need for professional guidance and caution due to the complexities of individual patient conditions.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Cases of Parkinson’s Disease | As Parkinson’s disease cases are increasing, the search for effective therapies continues. |
| Potential Benefits of Psilocybin | Psilocybin has shown promise in improving mood, cognition, and motor symptoms in patients. |
| Study Overview | A small pilot study involved 12 participants with mild to moderate Parkinson’s aged 40-75. |
| Dosage and Effects | Participants received two doses of psilocybin and reported significant improvements after treatment. |
| Mood and Motor Symptoms Connection | Mood disorders are linked to faster physical decline in Parkinson’s patients. |
| Side Effects | Common side effects included anxiety and nausea, but were generally mild. |
| Future Research | A larger study is planned to rigorously test the efficacy of psilocybin on Parkinson’s disease. |
| Caution Advised | Experts recommend caution for Parkinson’s patients considering psilocybin due to early-stage research. |
Summary
Psilocybin in Parkinson’s Disease is receiving growing attention as researchers explore its potential benefits for individuals suffering from this challenging condition. Recent studies indicate that psilocybin, derived from certain mushrooms, may improve mood, cognition, and even motor symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s. As traditional treatments often fall short, the initial findings present a promising avenue for therapy. However, caution is urged, as this investigation is in its early stages, and further, rigorous trials are necessary to fully understand the effects and safety of psilocybin in this context.